Page 30 - SRPSKO DRUŠTVO ISTRAŽIVAČA RAKA
P. 30
Serbian Association for Cancer Research SDIRSACR
gold standard in EVs purification is ultracentrifugation, especially with density gradient. However, it is very difficult
to standardize all of the ultracentrifugation parameters that can affect the quality of isolated material and in this
sense, it is nearly impossible to set up a universally standardized protocol. Furthermore, the variability among sample
populations from the same cells and especially different sources renders this standardization even more difficult.
Ultracentrifugation is a low-throughput method and often samples, especially from plasma are contaminated with
lipoproteins, protein aggregates and other particles of similar size or density making them incompatible with clinical
utilization. There is emerging experimental evidence that substantial amounts of EVs RNA and proteins are lost during
ultracentrifugation. Additionally, using ultracentrifugation as a method of choice makes scaling-up extremely difficult if
not completely unobtainable. Immuno-affinity-based techniques offer an advantage of selecting pathology-specific EVs
and preserving them intact. Unfortunately, elevated costs and time constraints related to production of monoclonal
antibodies, as well as their large dimensions render them inappropriate for scalable and high-throughput EV isolation.
Recent scientific endeavors are aimed at developing versatile, cost-effective methodologies for scalable isolation (μL to
mL; mL to >L) of high-purity EVs from bio-samples, which are urgently needed to open new perspectives in EVs-based
theranostics. Novel methods for EV isolation based on single-domain antibodies as selective agents have been proven
effective for various biological sources such as plasma and urine(33, 34, 35).
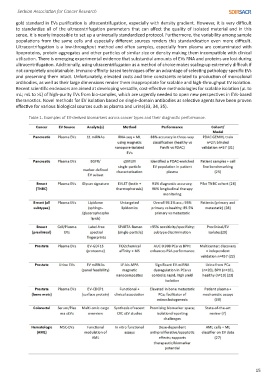
Table 1. Examples of EV-derived biomarkers across cancer types and their diagnostic performance.
15